Science
-
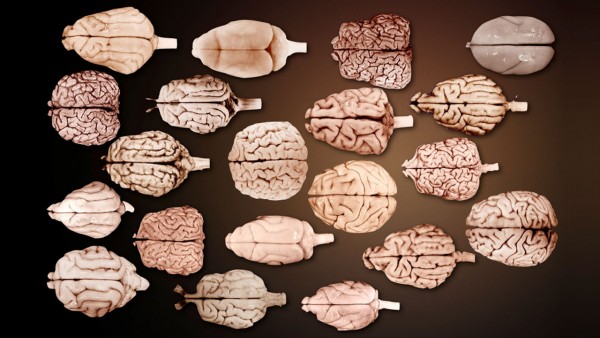
Your brain is like a wad of paper
Whether they’re from humans, whales, or elephants, the brains of many mammals are covered with elaborate folds. Now, a new study shows that the degree of this folding follows a […]
-
Why a pandemic flu shot caused narcolepsy
The 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic left a troubling legacy in Europe: More than 1300 people who received a vaccine to prevent the flu developed narcolepsy, an incurable, debilitating condition that causes overpowering daytime sleepiness, sometimes accompanied by […]
-
Sorting cells through levitation
What looks like a row of drifting gumdrops could hold a wealth of information for both clinical researchers and bench scientists. A team of bioengineers and geneticists has designed a […]
-

Newly identified brain structure may explain why parrots are such good copycats
Scientists say they have pinpointed the neurons that turn these birds into copycats. The discovery could not only illuminate the origins of bird-speak, but might shed light on how new […]
-

Huge study links wastewater injection wells to earthquakes
Before 2008, Oklahoma experienced roughly one noticeable earthquake per year. By 2014, that number had soared to almost one a day, and the state is not alone. Scientists have documented […]
-

Chimps caught drinking after hours
Alcoholic beverages are imbibed in nearly every human society across the world—sometimes, alas, to excess. Although recent evidence suggests that tippling might have deep roots in our primate past, nonhuman […]
-
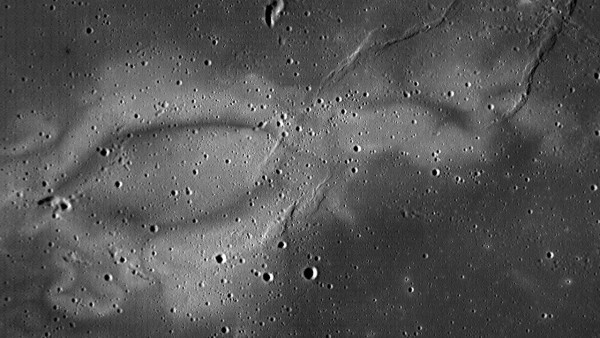
Comet impacts may explain mysterious swirls on moon
Light-colored swaths of terrain may be a side effect of comets striking the moon
-

Some chimpanzees infected with AIDS virus may harbor protective, humanlike gene
A gene has been found for what’s known as the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)—cell surface molecules that help the immune system recognize foreigners—that was remarkably similar to one in humans that […]
-
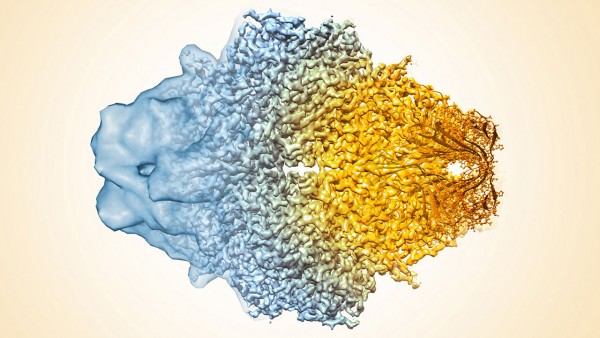
Electron microscopes close to imaging individual atoms
Researchers report that they’ve created the highest ever resolution cryo-EM image, revealing a druglike molecule bound to its protein target at near atomic resolution.
