Newsweek
-

The Dirty Truth About ‘Organic’ Produce
Passionate advocates of organic farming and foods resemble members of a religious cult, one founded on a «back to Nature» mentality. They are not so fundamentalist, however, that they do […]
-
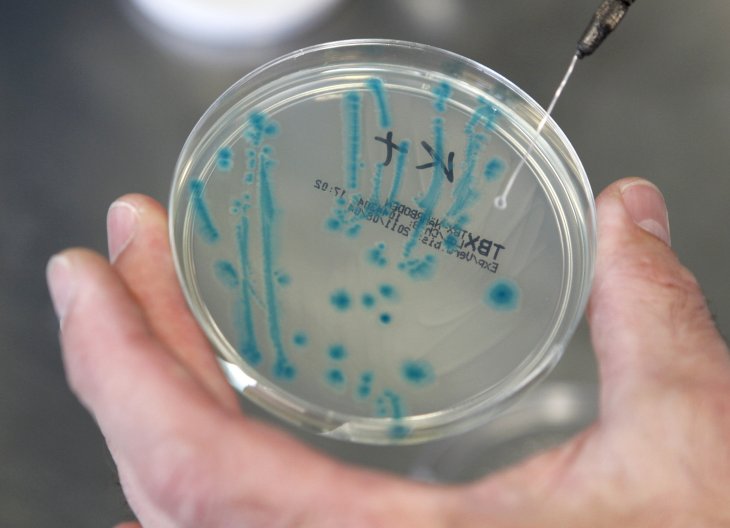
Distinctive Microbiome Associated With Schizophrenia
Scientists continue to discover ways that the viruses, bacteria and fungi that make a home in the human digestive system—also known as the human microbiome—may help further illuminate how the […]
-

Where and How Our Brains Store Memory
When somebody asks you to recount an experience, it’s common to begin with the time and place. Were you married in Cancún or Canton? In July or January? Having this […]
-
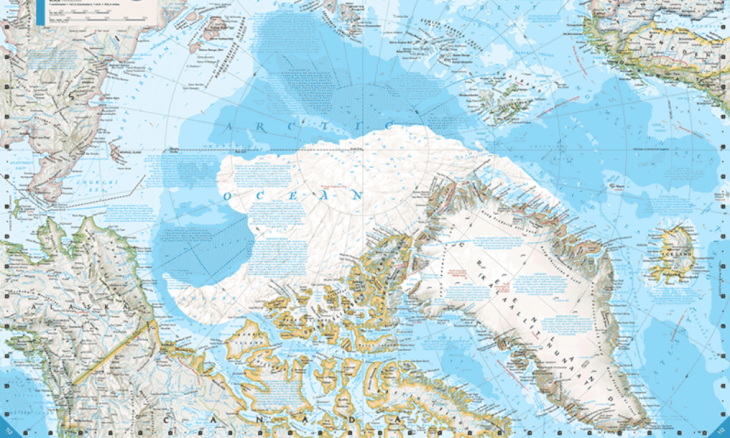
Watch How Much National Geographic Has Redrawn Its Atlas Because of the Melting Arctic
Last week, President Obama unveiled the final draft of sweeping new rules to limit emissions from the nation’s power plants. In his speech, he underlined the urgency of climate change […]
-
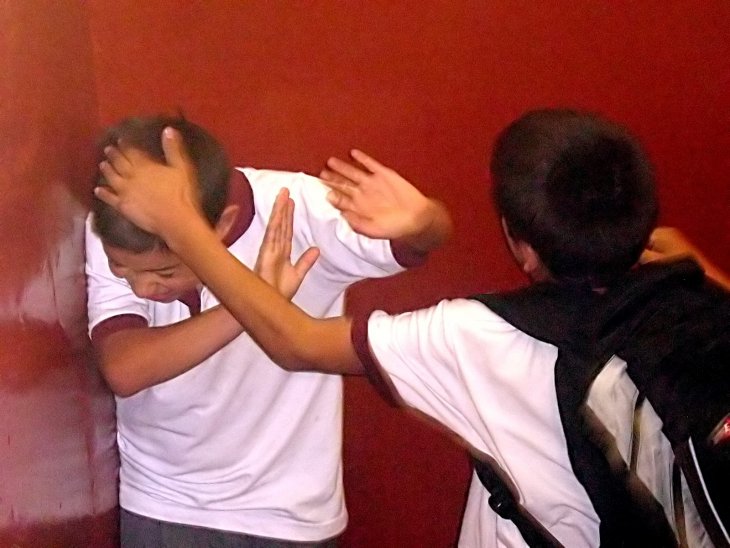

Bullies Have Higher Sex Appeal and Social Status, Says Study
Bullying is the scourge of classrooms and workplaces across the world. However, a recent study claims that bullying is an inherited evolutionary advantage which builds social status and even sex […]
-
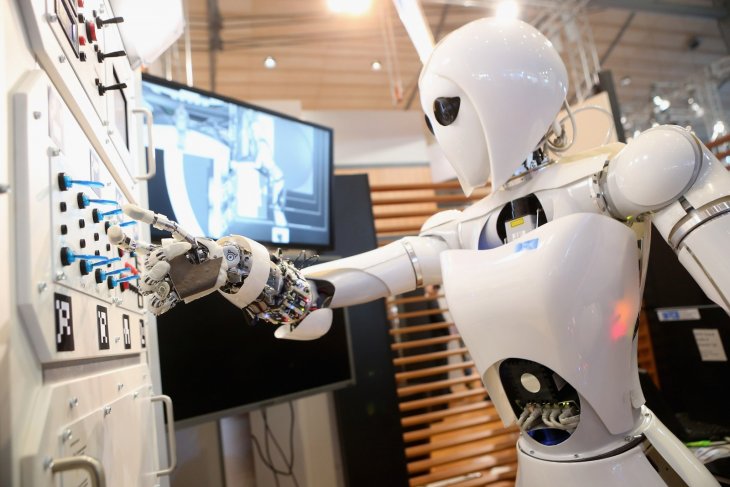

Technology doom sets in as artificial intelligence starts taking jobs
You know technology pessimism is getting serious when career technologists go rogue. Kentaro Toyama used to explore computer vision for Microsoft Research and co-founded Microsoft’s lab in India. He quit […]
-

Artificial pancreas could transform diabetes treatment
An artificial pancreas which automatically regulates blood sugar could revolutionise treatment for millions of diabetes sufferers across the world.
-
Could artificial intelligence kill us off?
Despite big differences about how best to conduct the search and where to look, several of the most persistent sleuths have found themselves disconcertingly close to agreement. No-one is yet […]
-
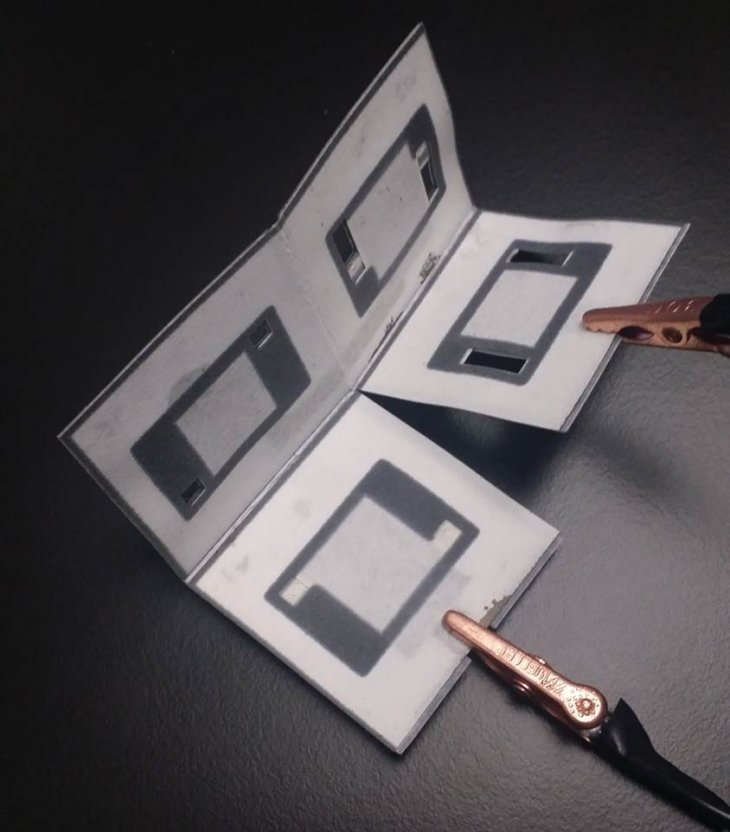
The foldable, five-cents battery powered by bacteria
A new origami paper battery, which is powered by bacteria and costs five US cents, could revolutionise the diagnosis of diseases in developing and remote areas.
