The Guardian
-

Touching robots can arouse humans
Researchers discover that touching the areas where a robot’s genitals or buttocks would be provokes a physiological response in humans
-

Genetically engineered ‘Magneto’ protein remotely controls brain and behaviour
“Badass” new method uses a magnetised protein to activate brain cells rapidly, reversibly, and non-invasively
-

Autism spectrum has no clear cut-off point, research suggests
New study published in Nature Genetics indicates that genes predisposing people to autism could influence social skills in the wider population
-

An update on a possible new particle from CERN’s Large Hadron Collider
As the LHC gets ready to start up again, two reananlyses of the data already taken look at last year’s intriguing hints…
-

Discovery of brainy T rex ancestor sheds light on dinosaur’s dominance
Skull found in Uzbekistan belonging to Timurlengia euotica, a horse-sized forerunner of Tyrannosaurus rex, reveals advanced brain and hearing ability that may have helped it become ‘king of the Cretaceous’ […]
-
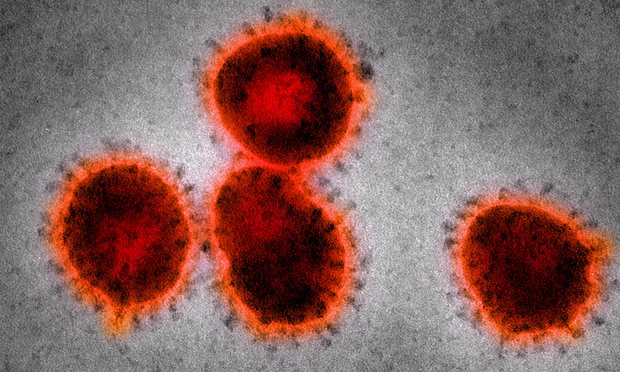
‘Ban’ on most hazardous virus experiments could be lifted this week
Experts meet in the US this week to thrash out fresh rules to govern studies which have the potential to create virulent and transmissible forms of viruses
-

Cancer tumour genetics reveal possible treatment revolution
Breakthrough could allow potent personalised treatments which prime patients’ own immune systems to attack biological markers on tumours
-
Zika virus: scientists present strong evidence of Guillain-Barré link
Findings published as experts warn that paralysing illness could overwhelm intensive care wards of Latin America
-

No monkeying around: toddlers as inventive as wild apes at using tools
Whether digging for insects or cracking nuts, children, like apes, work out how to use tools to solve problems without learning from others, research shows
